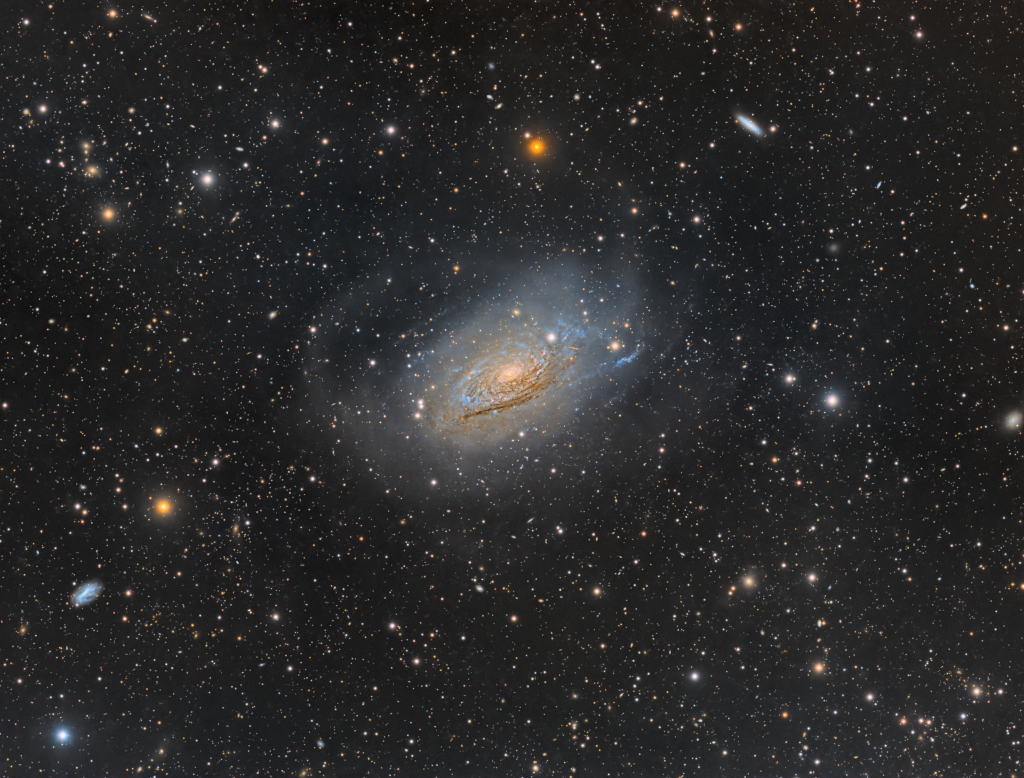
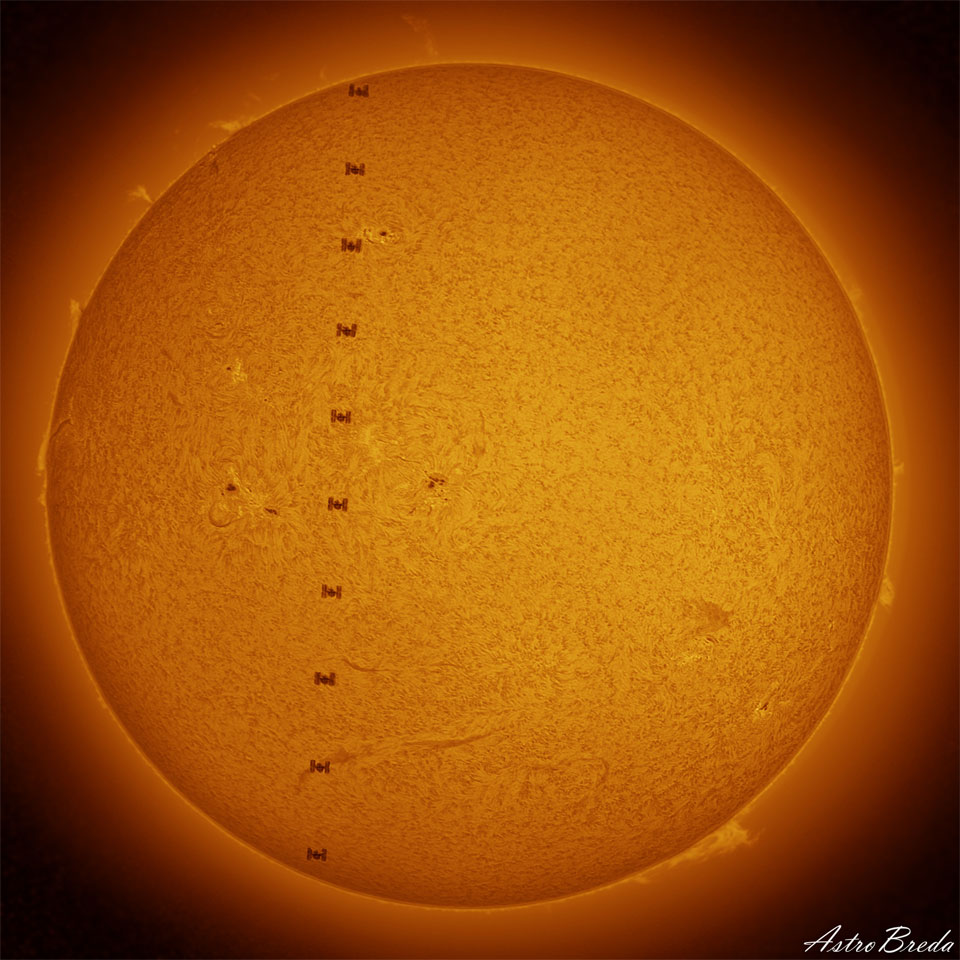
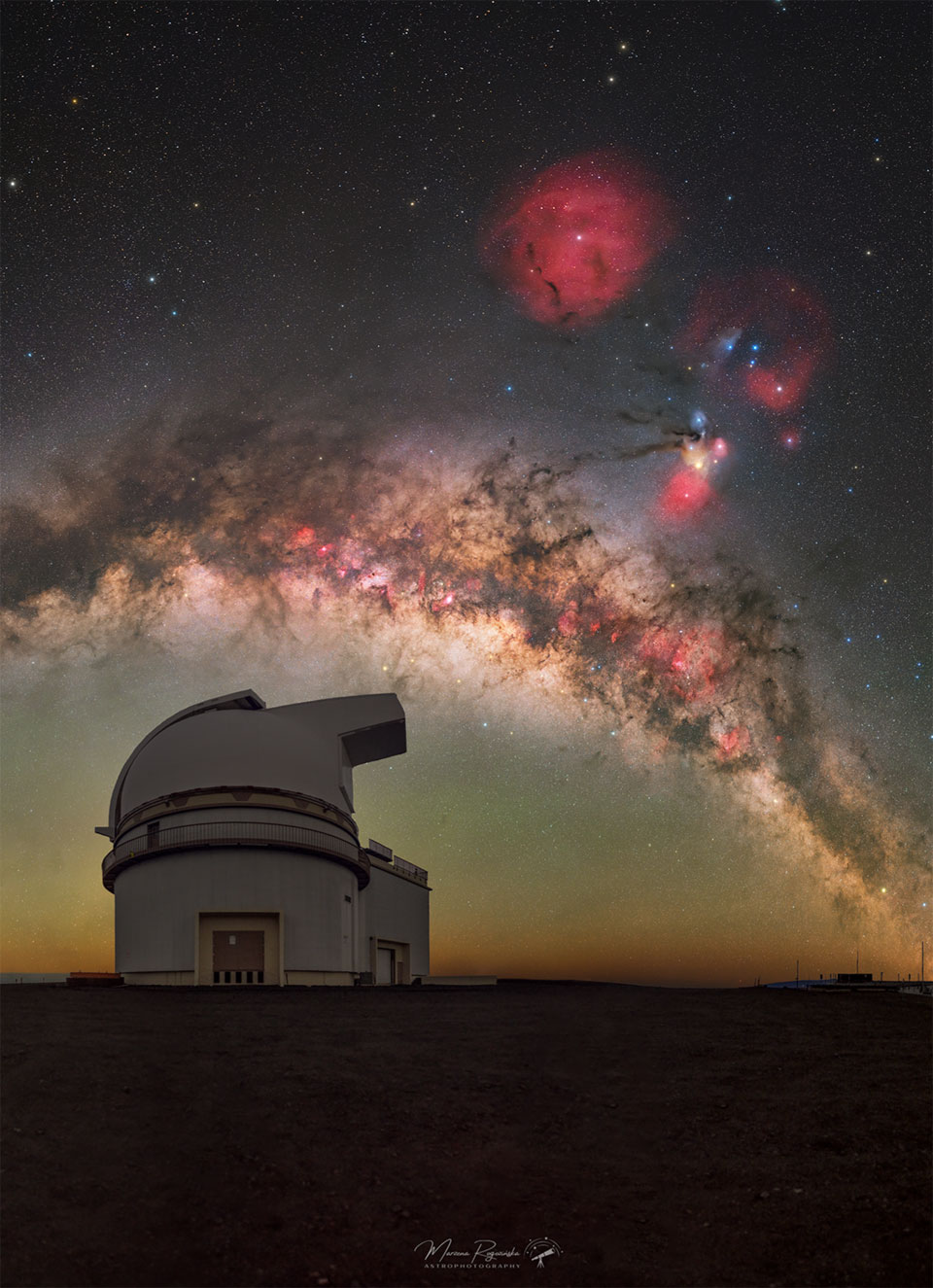
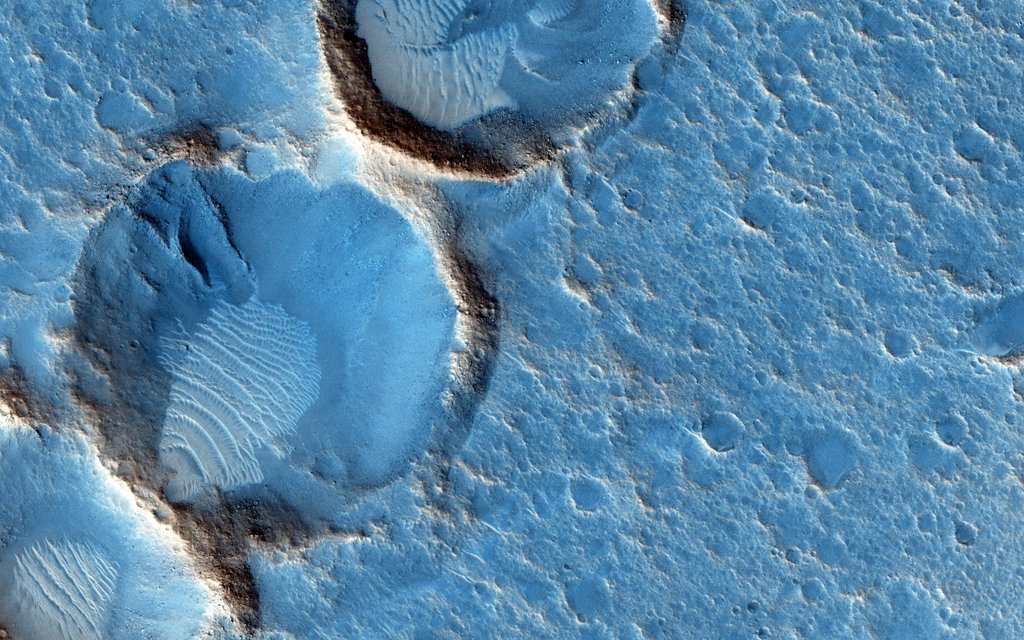
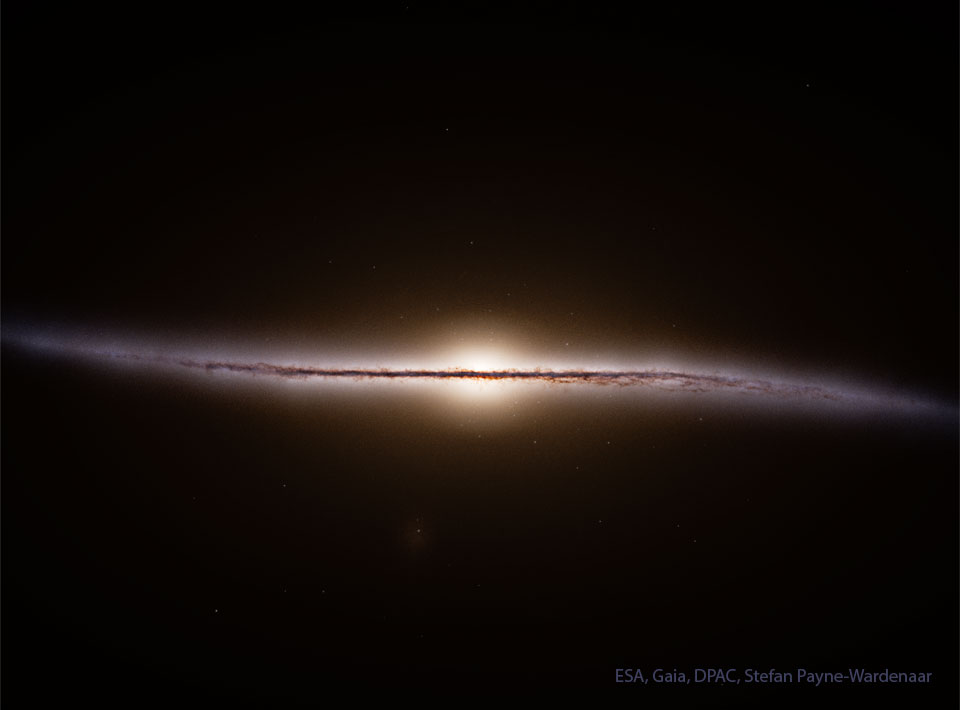
What's happening to this spiral galaxy? Although details remain uncertain, it surely has to do with an ongoing battle with its smaller galactic neighbor. The featured galaxy is labelled UGC 1810 by itself, but together with its collisional partner is known as Arp 273. The overall shape of UGC 1810 -- in particular its blue outer ring -- is likely a result of wild and violentgravitationalinteractions. This ring's blue color is caused by massive stars that are blue hot and have formed only in the past few million years. The inner galaxy appears older, redder, and threaded with coolfilamentary dust. A few bright stars appear well in the foreground, unrelated to UGC 1810, while several galaxies are visible well in the background. Arp 273 lies about 300 million light years away toward the constellation of Andromeda. Quite likely, UGC 1810 will devour its galactic sidekick over the next billion years and settle into a classic spiral form.
https://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap250601.html ( June 01, 2025)