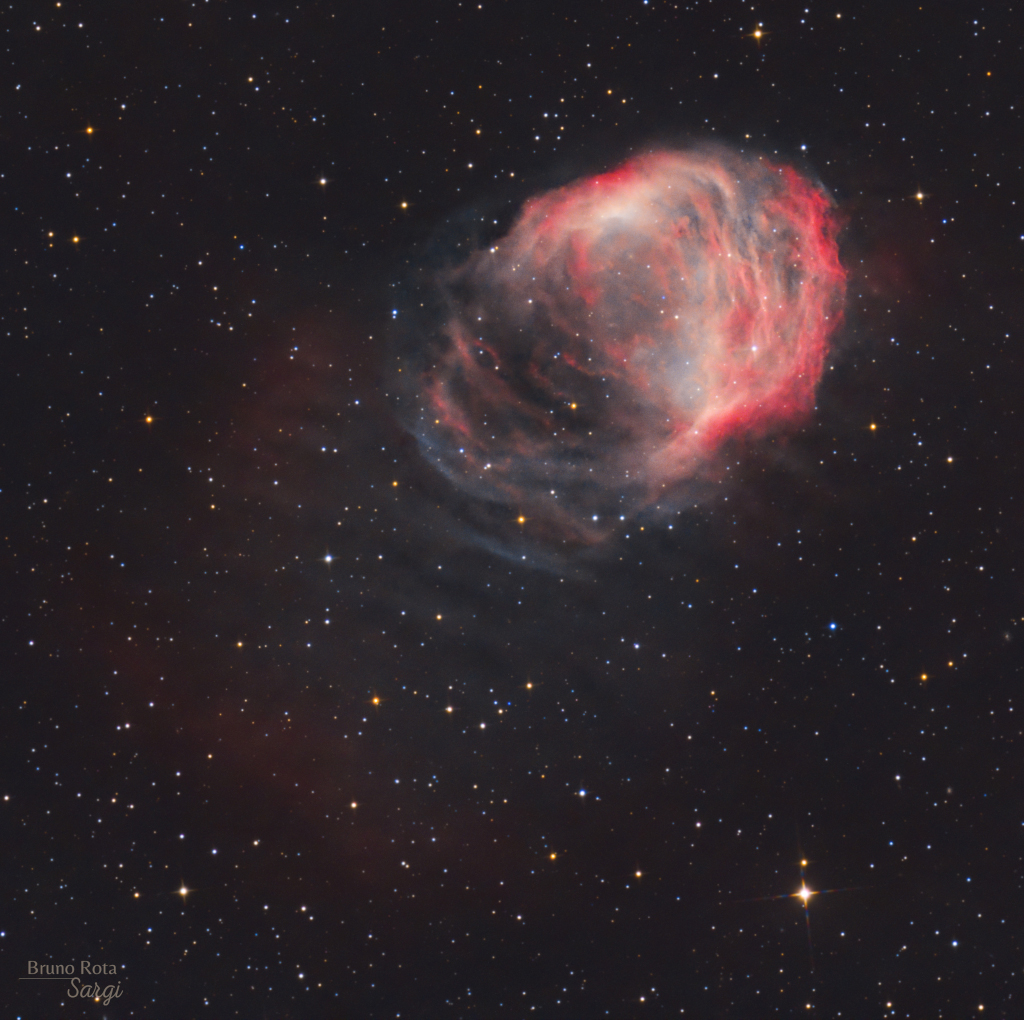
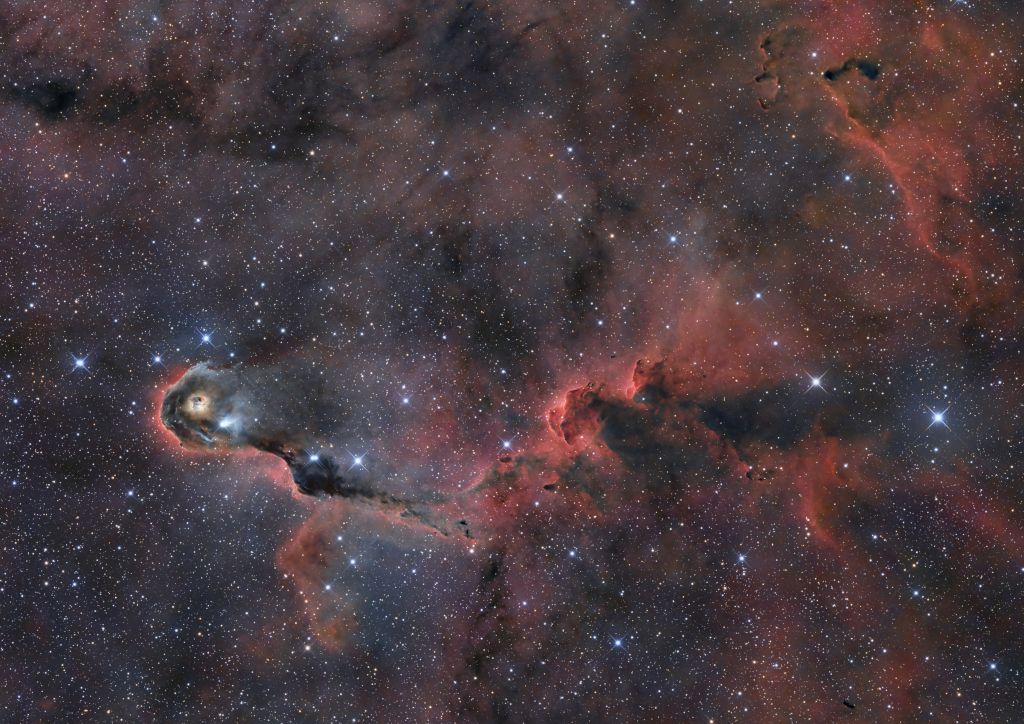
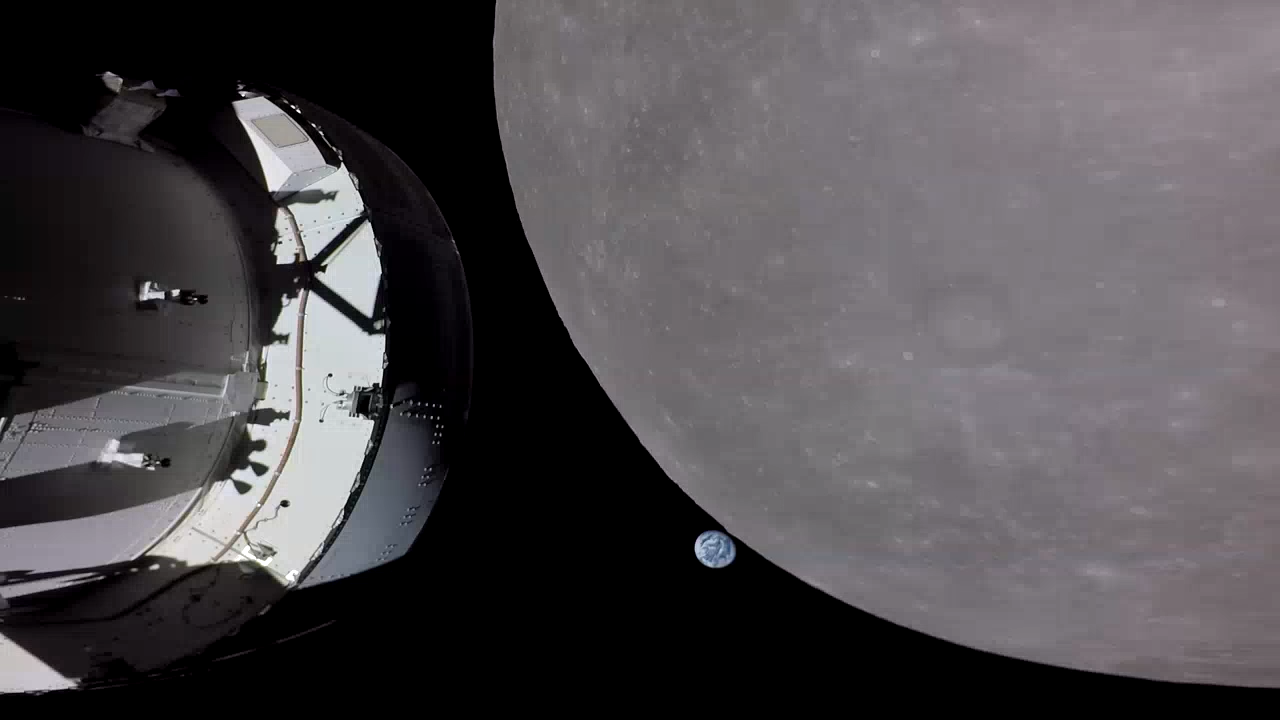
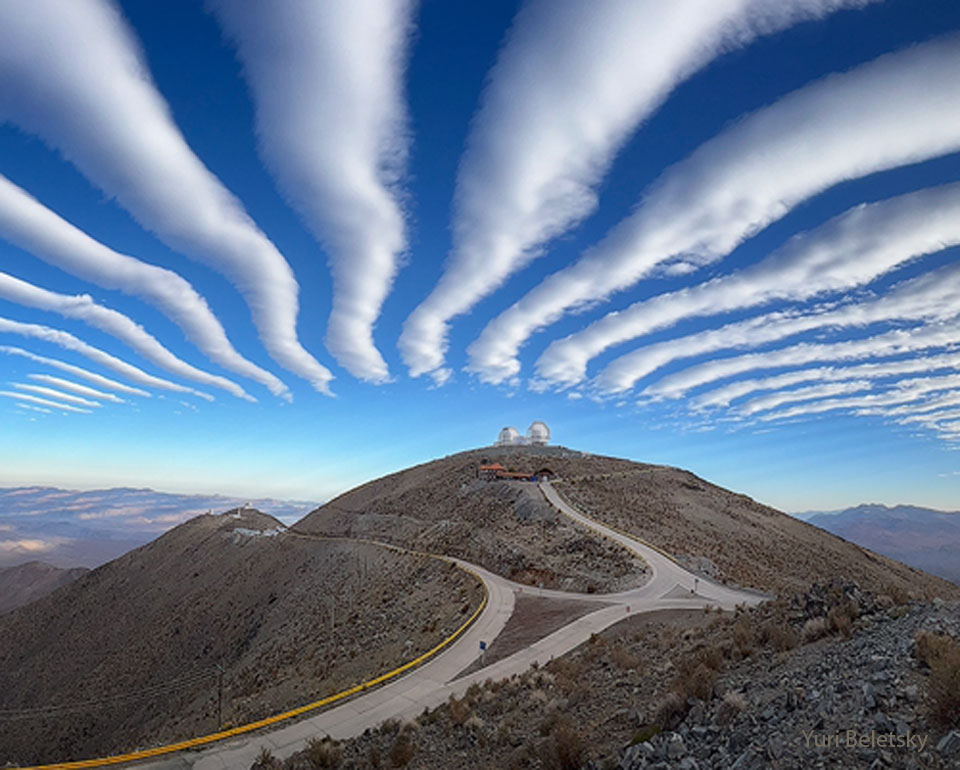
What color is the universe? More precisely, if the entire sky were smeared out, what color would the final mix be? This whimsical question came up when trying to determine what stars are commonplace in nearby galaxies. The answer, depicted here, is a conditionally perceived shade of beige. In computer parlance: #FFF8E7. To determine this, astronomers computationally averaged the light emitted by one of the larger samples of galaxies analyzed: the 200,000 galaxies of the 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey. The resulting cosmic spectrum has some emission in all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, but a single perceived composite color. This color has become much less blue over the past 10 billion years, indicating that redder stars are becoming more prevalent. In a contest to better name the color, notable entries included skyvory, univeige, and the winner: cosmic latte.
https://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap241201.html ( December 01, 2024)