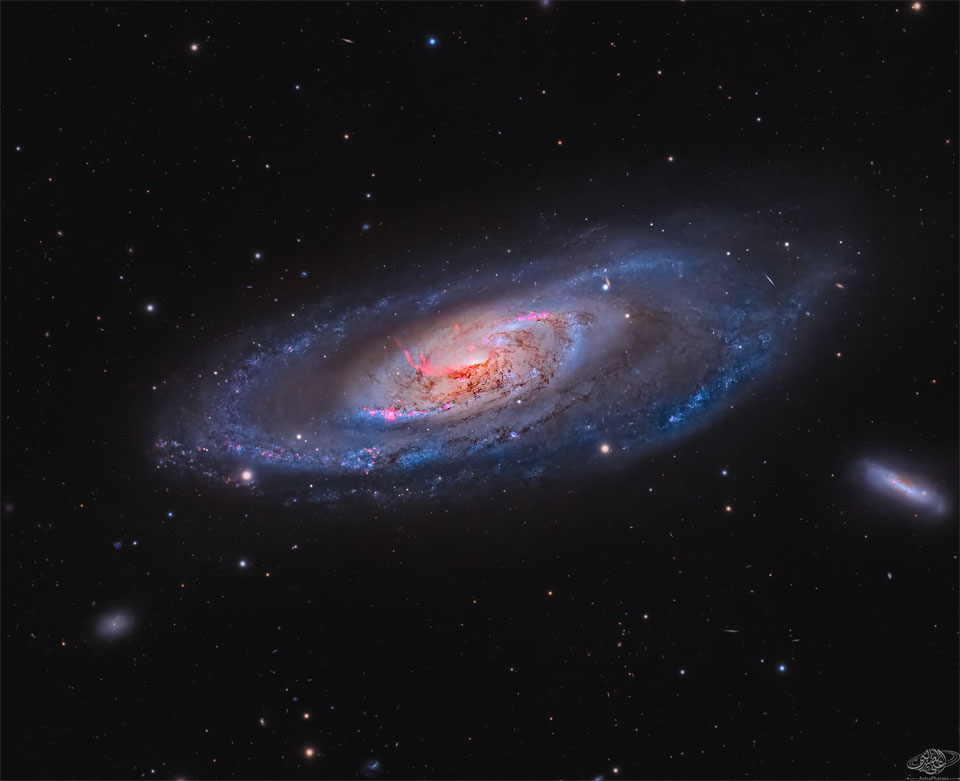
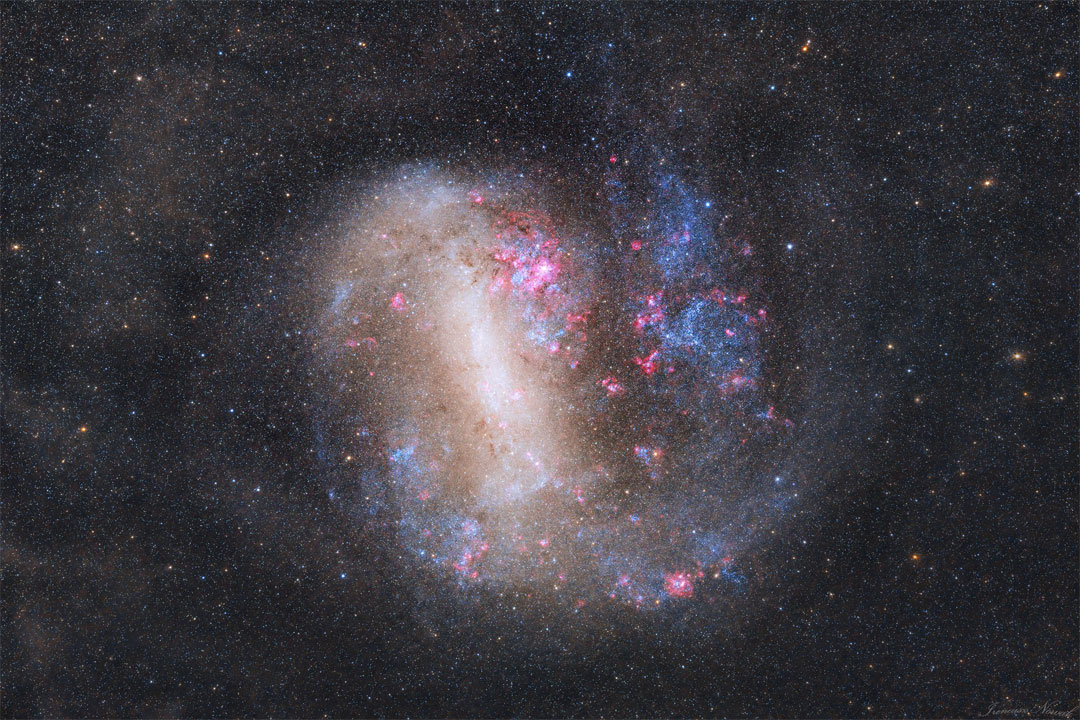
Big, beautiful spiral galaxy NGC 6744 is nearly 175,000 light-years across, larger than our own Milky Way. It lies some 30 million light-years distant in the southern constellation Pavo but appears as only a faint smudge in the eyepiece of a small telescope. We see the disk of the nearby island universe tilted towards our line of sight in this remarkably deep and detailed galaxy portrait, a telescopic image that spans an area about the angular size of a full moon. In it, the giant galaxy's elongated yellowish core is dominated by the light from old, cool stars. Beyond the core, grand spiral arms are filled with young blue star clusters and speckled with pinkish star forming regions. An extended arm sweeps past smaller satellite galaxy NGC 6744A at the upper left. NGC 6744's galactic companion is reminiscent of the Milky Way's satellite galaxy the Large Magellanic Cloud.
https://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap241101.html ( November 01, 2024)