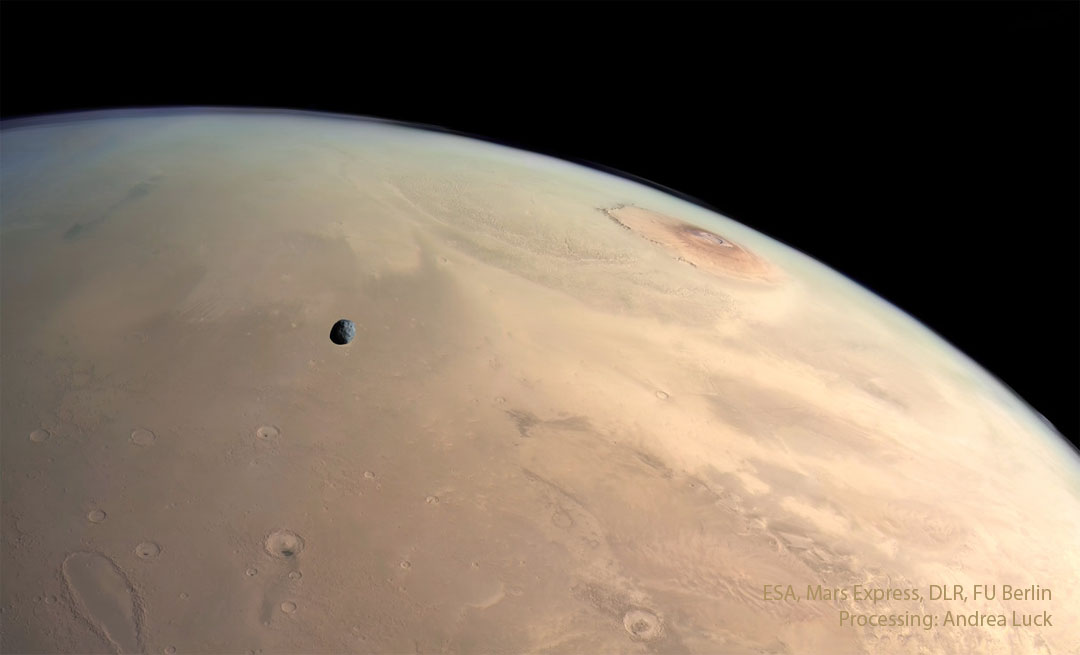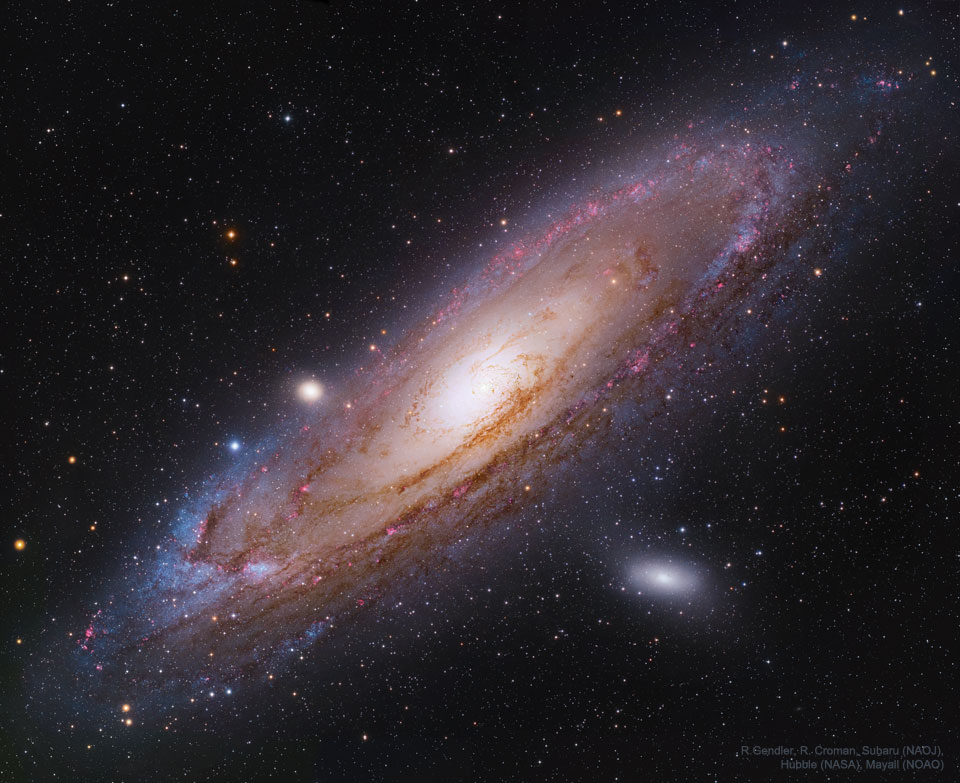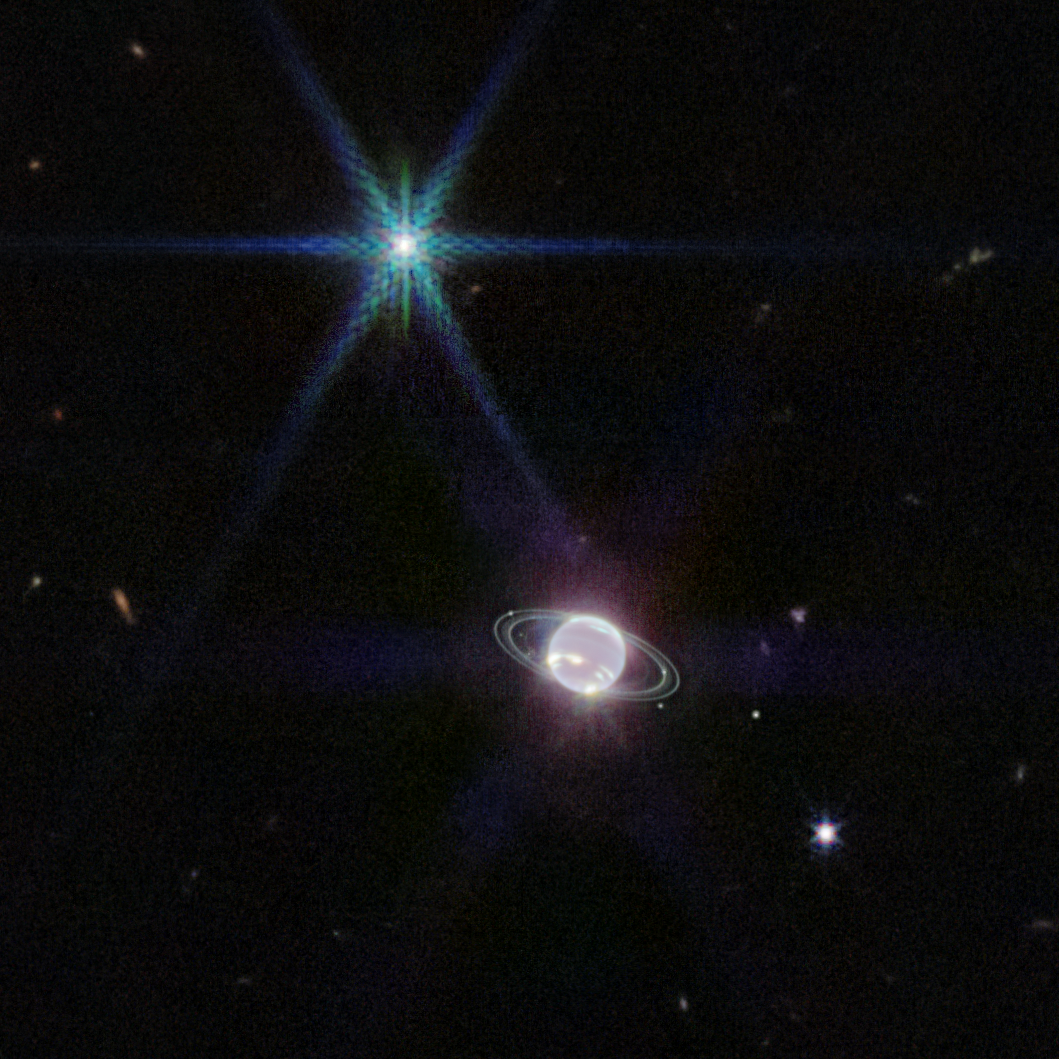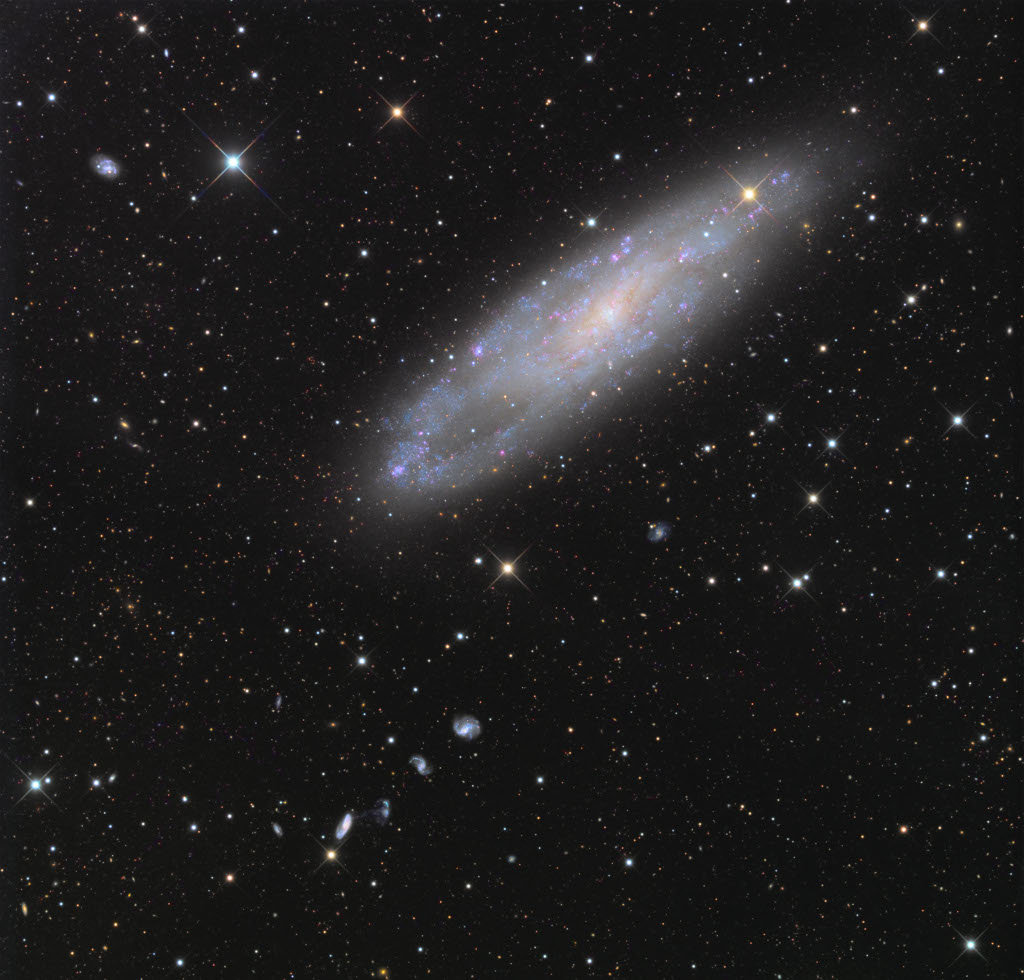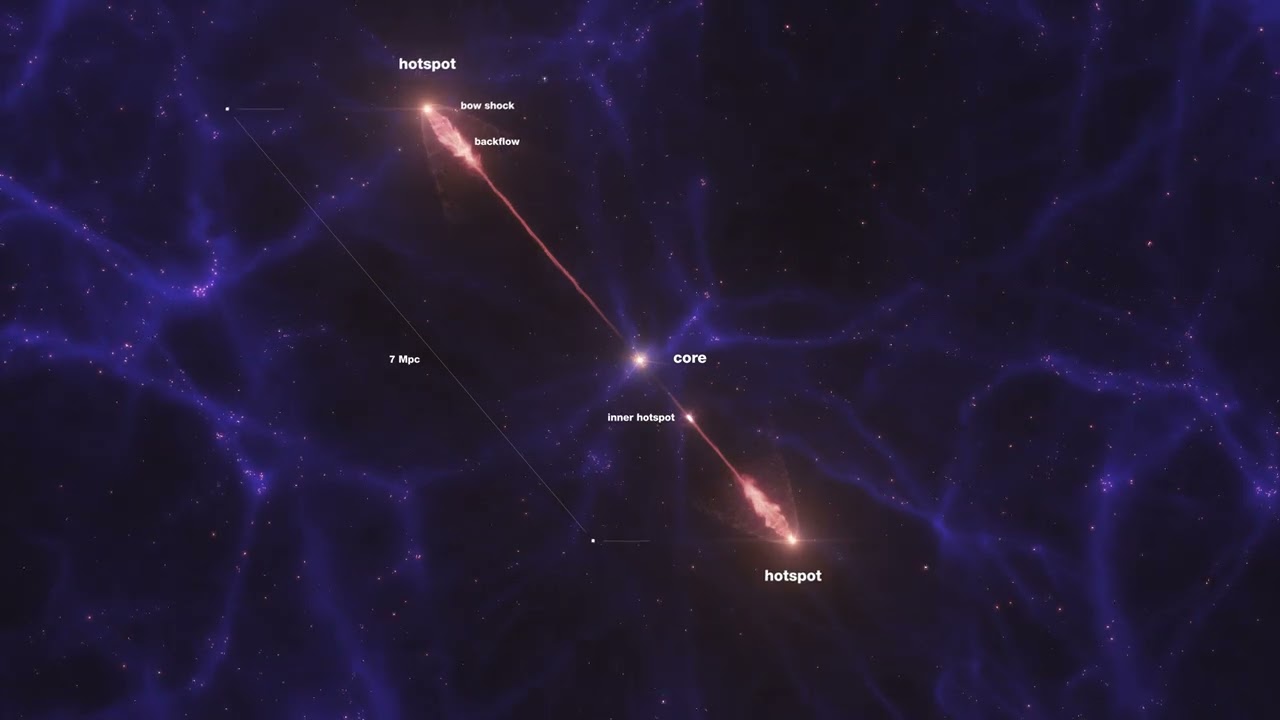
How far can black hole jets extend? A new record was found just recently with the discovery of a 23-million light-year long jet pair from a black hole active billions of years ago. Dubbed Porphyrion for a mythological Greek giant, the impressive jets were created by a type of black hole that does not usually create long jets -- one that is busy creating radiation from infalling gas. The featured animated video depicts what it might look like to circle around this powerful black hole system. Porphyrion is shown as a fast stream of energetic particles, and the bright areas are where these particles are impacting surrounding gas. The discovery was made using data from the Keck and Mayall (DESI) optical observatories as well as LOFAR and the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope. The existence of these jets demonstrates that black holes can affect not only their home galaxies but far out into the surrounding universe.
https://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap241001.html ( October 01, 2024)