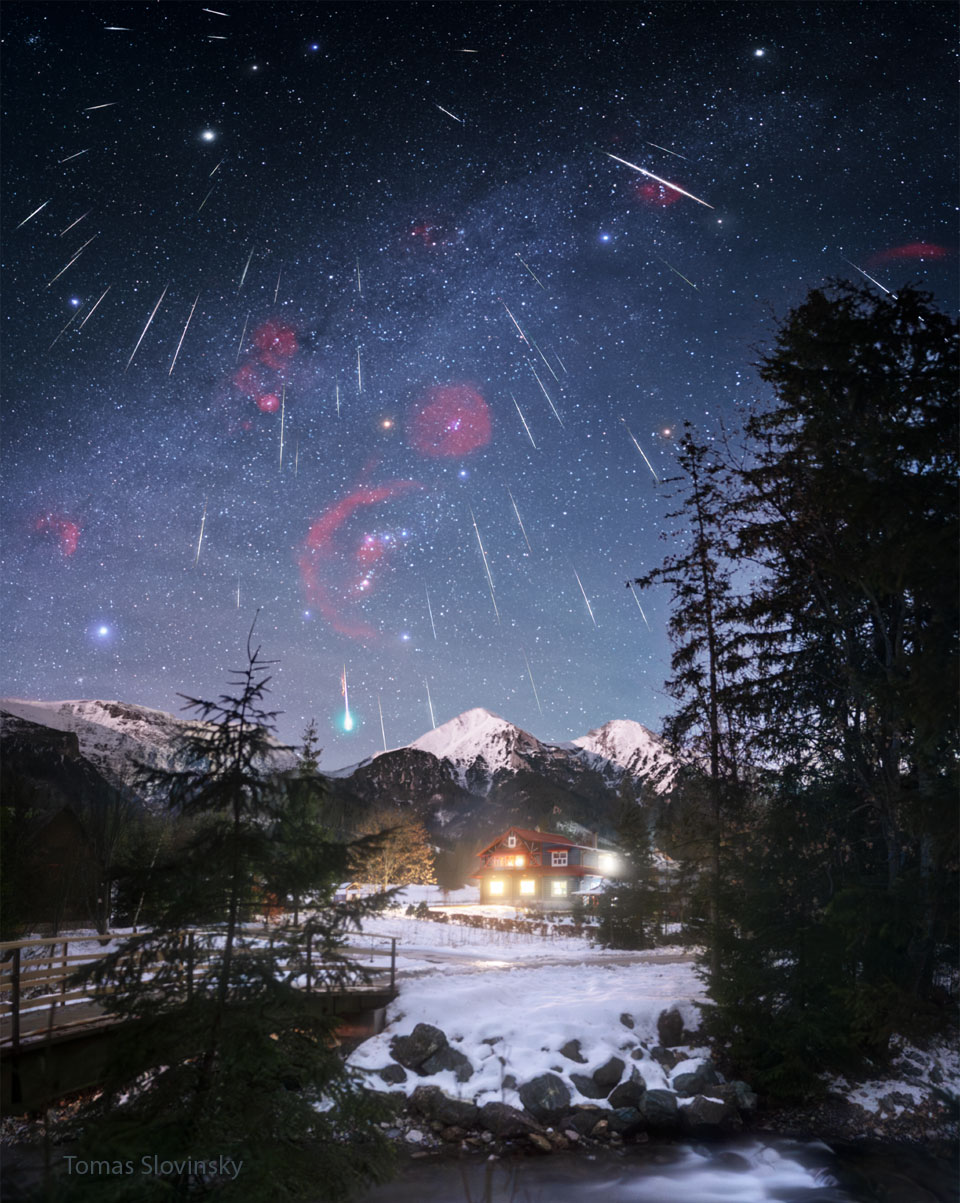
What’s happening over that tree? Two very different things. On the left is the Andromeda galaxy, an object that is older than humanity and will last billions of years into the future. Andromeda (M31) is similar in size and shape to our own Milky Way Galaxy. On the right is a red sprite, a type of lightning that lasts a fraction of a second and occurs above violent thunderstorms. Red sprites were verified as real atmospheric phenomena only about 35 years ago. The tree in the center is a boab, which may live for as long as a thousand years. Boab trees grow naturally in Australia and Africa and are known for being able to store large amounts of water: up to 100,000 liters. The featured image was captured last month near Derby in Western Australia.
https://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap251216.html ( December 16, 2025)